Heart palpitations, the sensation of a racing, pounding, or fluttering heartbeat, can be an unsettling experience. While often harmless, such heartbeat irregularities can sometimes indicate underlying cardiovascular issues or other health conditions.
What are heart palpitations, and what are the potential remedies? Understanding these heartbeat irregularities and exploring natural approaches, such as magnesium supplements, can provide valuable insights for managing this common cardiovascular concern.
This article will examine the relationship between magnesium deficiency and heart palpitations, focusing on the types of magnesium supplementation that may offer the most benefits for individuals experiencing irregular heartbeats.
Introduction to Heart Palpitations
What Are Heart Palpitations?
What are heart palpitations exactly? Heart palpitations are abnormal occurrences in which a person’s heartbeat manifests as a fluttering, racing, or pounding sensation in the chest, throat, or neck.
Most people experience occasional palpitations throughout their lives, and the majority are harmless. However, frequent episodes may indicate underlying issues that require medical attention.
Common Heart Palpitation Causes
Understanding heart palpitation causes is essential for determining the most effective treatment approach. The triggers for these irregular heartbeats vary widely and can include both lifestyle and medical factors.
Heart palpitations after eating represent one of the most common triggers. Large meals can cause palpitations as the body redirects blood flow to support digestion, which can temporarily affect the heart rhythm. Foods high in caffeine, sugar, or refined carbohydrates can also stimulate the cardiovascular system and trigger irregular heartbeats.
Additional common heart palpitation causes include:
- Stress and anxiety disorders
- Lack of sleep or chronic fatigue
- Intense physical exercise or overexertion
- Hormonal fluctuations
- Certain medications and dietary supplements
- Dehydration and electrolyte imbalances
- Magnesium, potassium, or calcium deficiency
- Thyroid disorders
- Low blood sugar levels
When to Worry About Heart Palpitations
While most palpitations are benign, knowing when to worry about heart palpitations is crucial for maintaining health and safety. A person should consult a specialist in cardiology or seek emergency care immediately if they experience:
- Chest pain, pressure, or tightness accompanying palpitations
- Severe shortness of breath or difficulty breathing
- Dizziness, lightheadedness, or fainting episodes
- Palpitations lasting more than several minutes
- Frequent episodes that interfere with daily activities
- Rapid heart rate exceeding 100 beats per minute at rest
- A family history of heart disease, sudden cardiac death, or arrhythmias
Understanding when to worry about heart palpitations also involves recognizing patterns. Palpitations that occur with increasing frequency, last longer than usual, or develop new accompanying symptoms should prompt medical consultation.
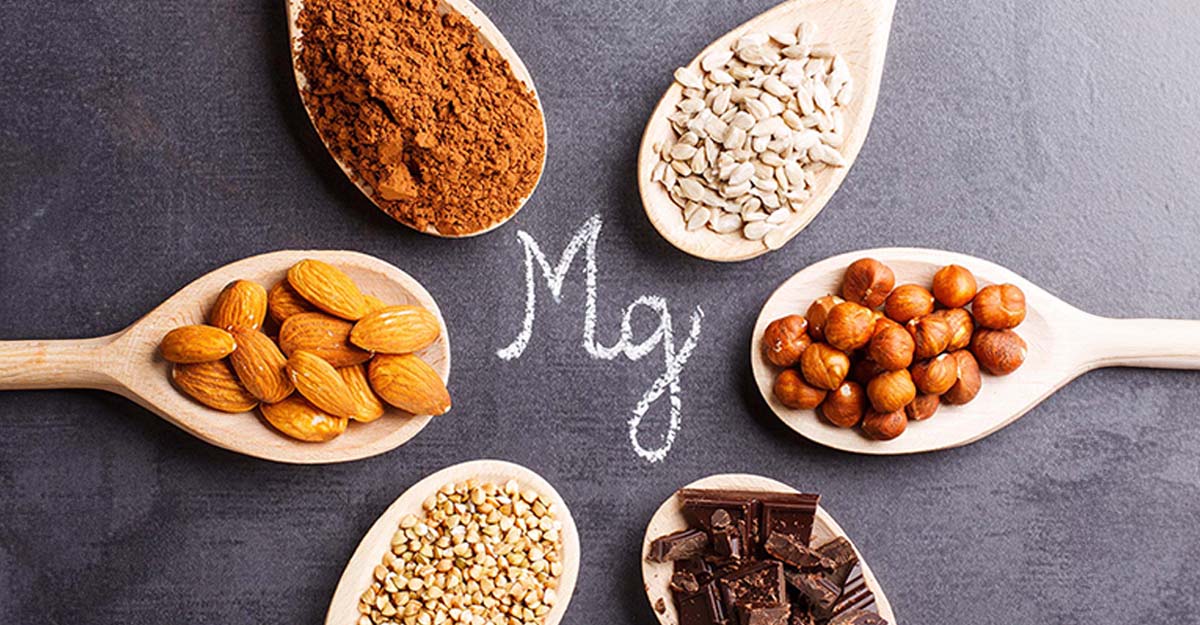
Different Types of Magnesium
What type of magnesium is best for heart palpitations? When considering magnesium supplements for cardiovascular support, understanding the various forms available helps ensure the selection of the most suitable option.
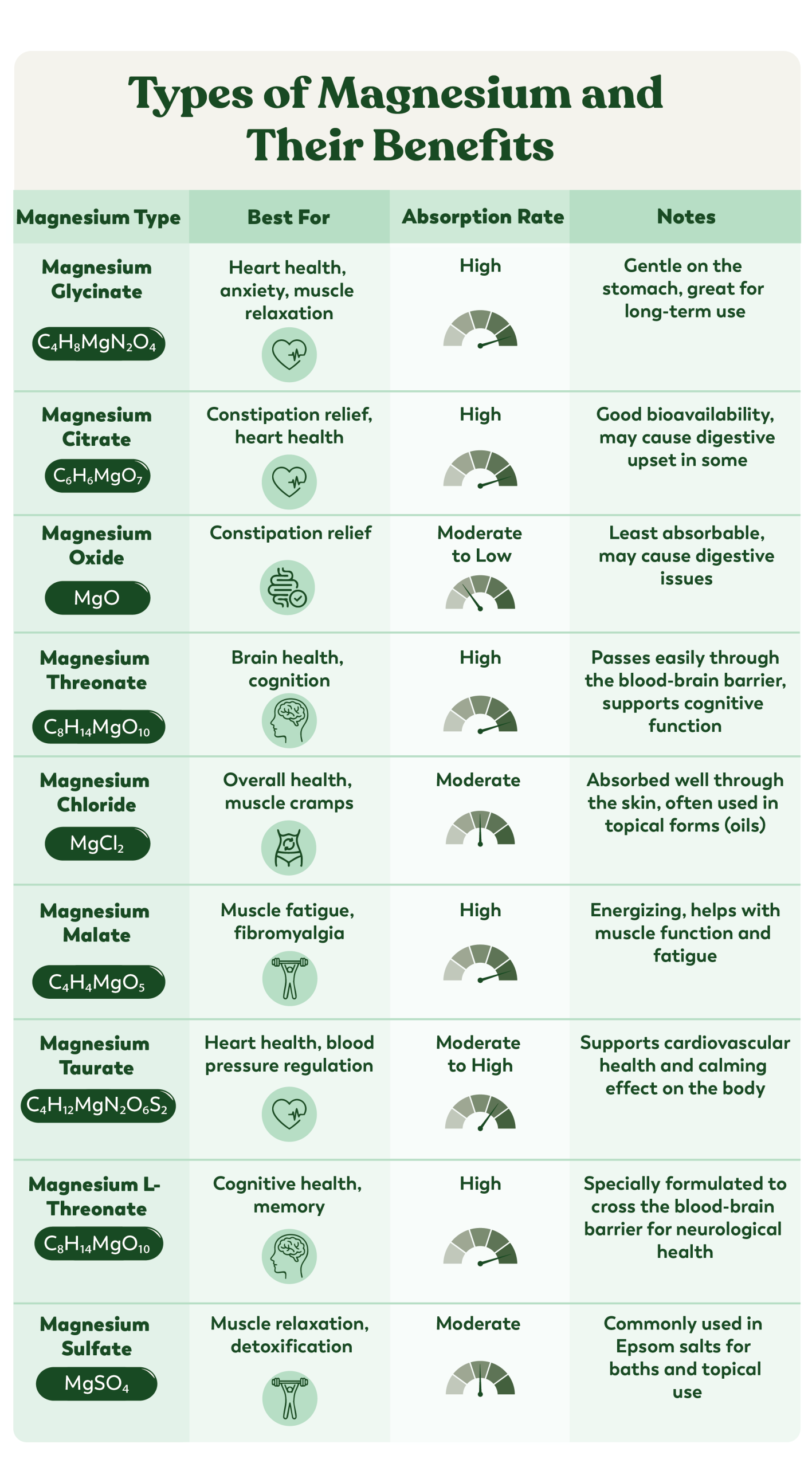
Overview of Common Forms of Magnesium Supplements.
- Magnesium Citrate is created by combining magnesium with citric acid. This form offers good bioavailability and is often recommended for those new to magnesium supplementation.
- Magnesium Oxide is inexpensive, but it has lower bioavailability compared to other forms. It is generally not the preferred choice for heart palpitations due to absorption limitations and potential digestive side effects.
- Magnesium Chloride offers excellent absorption and can be effective for raising magnesium levels in the body. This form can be beneficial for heart palpitations, especially when a deficiency is the underlying cause.
Absorption Rates and Other Health Benefits
When selecting the best magnesium for heart health, absorption rates should be taken into consideration.
Chelated forms of magnesium, where the mineral is bound to amino acids, generally offer superior absorption compared to inorganic forms. These chelated varieties are often gentler on the digestive system and provide sustained magnesium levels in the body.
The absorption rate affects how quickly and effectively the magnesium can address deficiency-related palpitations. Forms with higher bioavailability may provide faster relief and require lower doses to achieve therapeutic effects.
Best Magnesium Supplements for Heart Health and Palpitations
Selecting the best magnesium supplements for heart support requires understanding which forms offer optimal cardiovascular benefits, excellent absorption, and minimal side effects. The following summaries provide a detailed comparison.*
Magnesium Glycinate
Magnesium Glycinate is one of the best magnesium supplements for heart palpitations. This chelated form combines magnesium with the amino acid glycine, creating a compound that is gentle on the digestive system and highly bioavailable. Pure Encapsulations Magnesium (glycinate) offers excellent absorption with minimal gastrointestinal side effects, making it suitable for daily use.
The glycine component provides benefits beyond mineral delivery. Glycine has natural calming properties that complement magnesium’s cardiovascular support, making this combination potentially effective for anxiety and stress-related palpitations. Klaire Labs Magnesium Glycinate Complex also contains this formulation.
Magnesium Taurate
Magnesium Taurate represents another excellent choice for the best magnesium for heart palpitations. Taurine, an amino acid naturally found in heart muscle, works synergistically with magnesium to support cardiovascular function. Magnesium taurate is known to offer anxiety-related benefits. Cardiovascular Research Magnesium Taurate specifically targets heart health and helps maintain proper electrolyte balance.
Magnesium Citrate
Magnesium Citrate is known for good bioavailability and is often recommended for individuals new to magnesium supplementation. Pure Encapsulations Magnesium (citrate) offers pharmaceutical-grade quality, while Thorne Research Magnesium CitraMate combines citrate with malate for enhanced absorption and energy support. For convenient supplementation, Natural Vitality Calm Gummies Magnesium Citrate provides an easy-to-take format.
Magnesium Malate
Magnesium Malate combines magnesium with malic acid, supporting both cardiovascular health and energy production. Xymogen OptiMag Neuro Powder is available in a convenient powder format. For comprehensive support, Vital Nutrients Magnesium (glycinate/malate) 120 Mg combines two highly bioavailable forms in one supplement.
Magnesium L-Threonate
Magnesium L-Threonate offers unique benefits for individuals experiencing stress-related palpitations. This form crosses the blood-brain barrier effectively, potentially helping with anxiety, which can trigger heart palpitations. Life Extension Neuro-Mag® Magnesium L-Threonate and Jarrow Formulas MagMind Magnesium L-Threonate both provide this specialized form.
Magnesium Orotate
Magnesium Orotate includes orotic acid, which may enhance the cardiovascular benefits of magnesium. Priority One Magnesium Orotate provides this specialized form for targeted heart support.
Additional products containing high-potency magnesium include Trace Minerals Research Mega-Mag 400 Mg and Standard Process E-Z Mg.
Finding the Best Magnesium for Anxiety and Heart Palpitations
The best magnesium for anxiety and heart palpitations involves forms that specifically support nervous system function while providing cardiovascular benefits. Anxiety and palpitations frequently occur together, creating a cycle where anxiety triggers palpitations, which then may worsen anxiety levels.
Magnesium glycinate stands out as potentially the best magnesium for anxiety and heart palpitations due to its dual-action approach. The glycine component has inhibitory neurotransmitter properties that promote relaxation and may help break the anxiety-palpitation cycle.
Magnesium taurate also offers anxiety-related benefits, as taurine has been studied for its calming effects on the nervous system. It may be an excellent choice for individuals whose palpitations are primarily stress or anxiety-related.
How Magnesium Affects Heart Health
Magnesium plays a vital role in numerous bodily functions. For cardiovascular health, it helps regulate heart rate, supports proper blood pressure levels, and maintains the electrical impulses that control heart rhythm.
Magnesium’s Role in Supporting Cardiovascular Function
Magnesium’s role in heart health works through several mechanisms that impact cardiac function. This vital mineral supports the delicate balance between calcium and potassium, which is essential for proper contraction and relaxation of the heart muscle.
Magnesium works synergistically with other minerals, such as potassium, found in foods like bananas, spinach, and black beans, to maintain proper electrolyte balance, which is crucial for maintaining a stable heart rhythm.
When magnesium levels are adequate, the heart can maintain a steady rhythm and respond appropriately to physical and emotional stress. The mineral acts as a natural blocker, helping prevent excessive calcium from entering heart cells and causing irregular contractions.
Low levels of magnesium may contribute to various cardiovascular issues, including arrhythmias, high blood pressure, and increased risk of heart failure. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) recognizes the importance of magnesium for heart health, with the recommended dietary allowance varying based on age, gender, and health status.
The Connection Between Magnesium Deficiency and Heart Palpitations
Research suggests that magnesium for heart palpitations may be effective on a supplementary basis when deficiency is the underlying cause. Magnesium deficiency affects the heart’s electrical conduction system, potentially leading to irregular heartbeats in the ventricles or contributing to the development of atrial fibrillation.
Individuals taking certain medications are at an increased risk of developing a magnesium deficiency. Diuretics prescribed for blood pressure management can increase magnesium excretion through the kidneys. Additionally, individuals with cardiovascular disease may experience decreased magnesium levels due to increased urinary excretion, potentially affecting both blood sugar control and heart function.
Magnesium’s Impact on Reducing Anxiety
Beyond its direct cardiovascular effects, magnesium for heart palpitations also works by addressing anxiety, which frequently accompanies and can trigger palpitations. Magnesium helps regulate the nervous system and may reduce the stress response that often precipitates irregular heartbeats.
Magnesium supports the production of GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid), a neurotransmitter that promotes relaxation and calm. This dual action—supporting both heart rhythm and nervous system function—makes magnesium valuable for managing palpitations, especially when they’re stress-related.
Dosage and Safety
Choosing the best magnesium for heart health and using the proper dosage go hand in hand. Determining the appropriate dosage for magnesium supplements depends on individual factors, including current magnesium status, dietary intake, and specific health goals.
The recommended dietary allowance for magnesium ranges from 310 to 420 mg daily for most adults, but therapeutic doses for heart palpitations may vary.
Recommended Dosages for Managing Heart Palpitations and General Heart Health
Men aged 19–30 require approximately 400 mg daily, while men over 30 need 420 mg. Women aged 19–30 require 310 mg daily, and women over 30 need 320 mg. Pregnant and breastfeeding women have higher requirements, ranging from 350–400 mg daily.
When addressing heart palpitations, healthcare providers may recommend higher doses initially to correct the deficiency, followed by maintenance dosing. Some individuals may benefit from doses ranging from 200–600 mg daily, depending on their specific needs and tolerance.
Begin with lower doses and gradually increase them to assess tolerance and effectiveness. Beginning with 200–300 mg daily allows a person to monitor their body’s response and adjust accordingly.
Potential Side Effects and Precautions
When selecting the best magnesium for heart palpitations, it is also essential to be informed about the potential side effects and precautions associated with magnesium supplements. The most common side effects are gastrointestinal and typically occur with higher doses or certain forms of magnesium.
Digestive side effects may include diarrhea, nausea, and abdominal cramping. These effects are more common with magnesium oxide and less likely with chelated forms, such as magnesium glycinate or taurate.
Individuals with kidney disease should exercise particular caution with magnesium supplementation, as impaired kidney function can affect magnesium clearance. Magnesium supplements can interact with certain medications, including some antibiotics, diuretics, and heart medications.
Conclusion
Understanding the connection between magnesium deficiency and heart palpitations empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their cardiovascular health. The best magnesium supplements for heart palpitations typically include highly bioavailable forms, like magnesium glycinate, taurate, or citrate.
Key Takeaways on the Best Magnesium Supplements for Heart Palpitations
The most effective use of magnesium for heart palpitations involves selecting the correct form based on an individual’s needs, tolerance, and specific symptoms.
Magnesium glycinate offers excellent absorption with minimal digestive side effects, making it suitable for daily use and managing anxiety-related palpitations.
Magnesium taurate provides targeted cardiovascular support through the synergistic effects of both magnesium and taurine. For those new to supplementation, magnesium citrate offers good bioavailability.
Tips on Consulting a Healthcare Provider Before Starting Supplementation
Choosing the best magnesium for heart health represents just one aspect of comprehensive care, as professional guidance often proves essential for addressing underlying causes.
Before beginning any supplementation program, especially if a person has an existing cardiovascular disease or takes medications for blood pressure or heart conditions, consulting with a healthcare provider is essential. A cardiologist can evaluate an individual’s specific situation and recommend appropriate testing to rule out underlying heart conditions.
Whether dealing with occasional palpitations or seeking preventive support for cardiovascular health, incorporating appropriate magnesium supplements alongside a heart-healthy lifestyle may make a meaningful difference.
For additional guidance, refer to our comprehensive guide Which Magnesium is Right for Me? and our article Can You Take Calcium and Magnesium Together?
FAQs
What is magnesium’s role in heart palpitations?
Magnesium helps regulate heart rhythm and supports overall heart muscle function. It maintains the balance of electrical impulses in the heart, which may help prevent and alleviate heart palpitations. When magnesium levels are adequate, the heart can maintain steady contractions and regulate its proper rhythm.
What type of magnesium is best for heart palpitations?
The best magnesium for heart palpitations includes Magnesium Glycinate, Taurate, Citrate, Malate, L-Threonate, and Orotate. Each form offers unique benefits, with glycinate and taurate being particularly effective for cardiovascular support due to their high bioavailability and heart-specific benefits.
What are common signs of magnesium deficiency?
Magnesium deficiency ranks among the most common heart palpitation causes. Signs include muscle cramps, fatigue, irregular heartbeat, and increased susceptibility to stress and anxiety, which can trigger heart palpitations.
Is magnesium supplementation safe for heart health?
Magnesium supplements are generally safe for heart health when taken in recommended doses. However, it is essential to consult a healthcare provider before starting supplementation, especially for people with kidney issues, cardiovascular disease, or those taking medications that may interact with magnesium.
What’s the recommended daily magnesium intake?
The recommended dietary allowance for magnesium varies by age and gender, typically ranging from 310–420 mg for most adults. However, individual needs may vary based on health status, dietary magnesium intake, and specific therapeutic goals. A healthcare provider may help determine the appropriate dosage for an individual’s specific situation.
Can heart palpitations after eating be related to magnesium?
Yes, heart palpitations after eating may be related to a magnesium deficiency, especially if meals are large or high in refined carbohydrates, which can affect mineral absorption. Adequate magnesium levels help maintain a steady heart rhythm even during the increased metabolic demands of digestion.
When should I worry about heart palpitations?
A person should be concerned about heart palpitations if they are accompanied by chest pain, shortness of breath, dizziness, or fainting. Frequent episodes, palpitations lasting more than a few minutes, or those occurring with a family history of heart disease, warrant immediate medical evaluation by a cardiologist.
*FDA disclaimer: these product descriptions have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration, and these products are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.
* These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. The products mentioned are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.





